Example: set response header and body
You can use the WSHeader attribute to specify a response in a header. Return values without the attribute are sent in the body.
Note:
A message body is required when you perform an HTTP operation on a resource returning a value, otherwise the response results in the error-9106.
Example responses in header and body
PUBLIC FUNCTION help()
ATTRIBUTES (WSGet,
WSPath='/help')
RETURNS (INTEGER ATTRIBUTE(WSHeader),
STRING)
RETURN 3, "Hello world"
END FUNCTIONThe help function's RETURNS clause has two return values. An integer that is
returned in a header is specified with the WSHeader attribute. The string is
returned in the body.
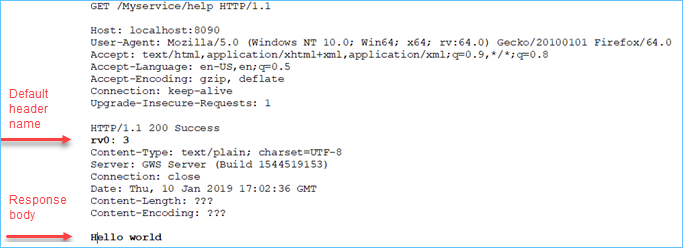
In the output the header is given a default name, "rv0", at runtime. You can change default
header naming via the WSName attribute, for example with:
RETURNS (INTEGER ATTRIBUTE(WSHeader, WSName="MyHeader"), STRING)